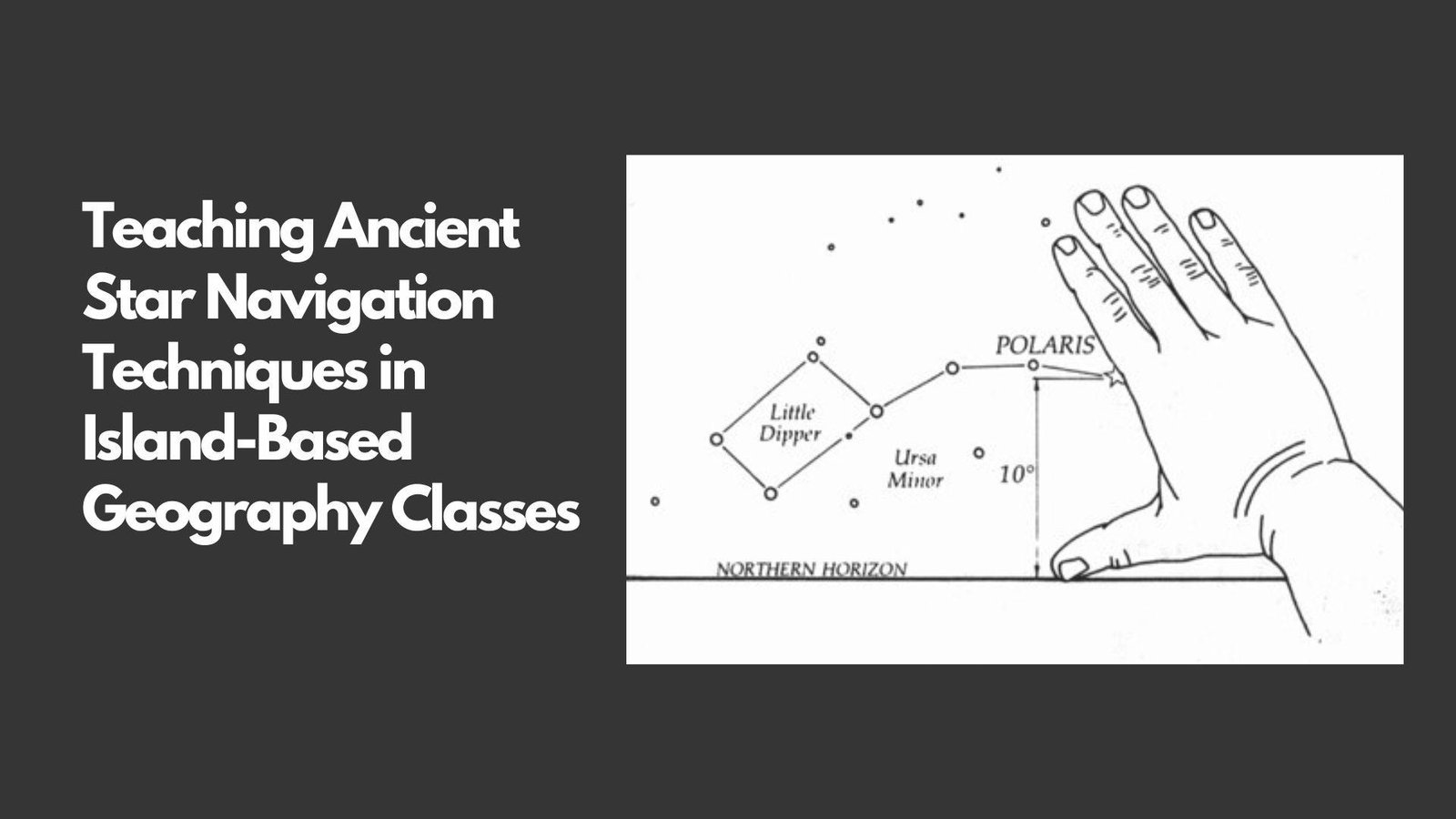
Integrating traditional arts and crafts in the elementary education can be a creative means of teaching standard subjects. Such creative approach can be the use of traditional pottery to teach simple geometric learning. Instead in pottery shapes figures curves and angles some which can be studied with geometric lessons are created. This cross- disciplinary approach enriches math lessons in students’ interaction and also serves a cultural- historical purpose.
The Link Between Pottery and Geometry
Most of the traditional pottery particularly in cultures that have had a long history of pottery work have their artifacts symmetrical in shapes, patterns and designs on the pottery. Most of these elements are derived from simple geometric principles including circles, spheres, cylinders, polygons and the like. Geometrical concepts become more import and meaningful hence their integration into a lesson through pottery is important. For instance the form of the pot can be described geometrically as circumference of the opening of the pot, height of the body of the pot and surface area of the external surface of the pot.
In mathematics, the teaching of geometry is characterized more in terms of drawing and equations rather informal generalization. But I have realized that many students fail to comprehend these concept or ideas especially when they only encounter them on paper. Through glazing various shapes of pots and making other related ones, geometry becomes quite tangible to student. They can learn about radius, diameter, symmetry, angles and proportions while making pottery shapes or making some types of pottery shapes hence understanding these is easy.
Integrating Pottery into Geometry Lessons
1. Introduction to Shapes and Symmetry
Teachers can start with common geometric shapes and features which should help the students learn quickly. Pottery can then be used as an example as to where these shapes are applied in real life objects. For instance, students may see the handle of a traditional pot and then notice that round shapes lie at the base of the pot, or that round shapes lie in the middle of the pot. Thus, we get the real life application for geometry as seen in the given picture.
A major element of the pottery design is the use of symmetry which can also be taught by availing objects for practice. Most of the usual pots have certain symmetrical features, and this is to present a chance to look at the reflection symmetry. The same can also be done by students where they are given the challenge to draw the symmetrical designs on clay or molding the shapes themselves.
2. Measuring Pottery Dimensions
Measurement is one of the skills that are associated with geometry. Pottery enables measurements of actual size such as height, width and even circumference among others among students. They can also use rulers and compasses and protractors to make geometrical measurements of a pot, as an example they would measure the area’s and volume’s. Through activities such as this, they are again able to build on shapes that exist in the three-dimensional world.
Another example of how this physical property can be incorporated into a Mathematics activity is if students were required to estimate how much clay would be required to fashion a given pot of a certain size and shape by calculating volume and surface area. As a result of this approach, students are able to reason with mathematics in such a way that they relate it with real-life situations.
3. Pottery Patterns and Tessellation
In the choice of designs on the pottery, they incorporate styles which are based on geometry. Geometric patterns are traditional pot shapes of a number of cultures; they are such patterns as triangles, squares or hexagons. This is a good time for teachers to explain tessellation; it is the process of laying flat shapes in such a manner that they do not allow gaps or overlap. It is possible to allow the students to try various geometric patterns on the body of the products placing art into the equation besides the mathematical one in the lesson.
4. Connecting Math with Cultural History
This is another strength of this approach in that the students get an opportunity to learn about cultural importance of pottery. Most of traditional pottery has social-cultural, religious or ceremonial importance to various societies at large. For instance, in Native American, African, and other Asian origins, people use pottery designs to express a number of cultural stories. This serves the purposes of widening the understanding of teachers on the cultural history and at the same time as a way of being able to impart the lessons related to geometry. Such an inter disiplinary learning prepares the learners to embrace the cultural diversity and at the same time enhances their mathematical understanding.
Benefits of Using Pottery in Geometry Lessons
The following are some of the advantages of using pottery while teaching geometry: It makes students to be more active in their learning as they are afforded an opportunity to understand concepts that would otherwise be regarded as difficult by embracing concrete experiences. This makes the learning process more practical as the students can have a closer look at the geometry and its applications. Also, the passages provided in art and culture combination with numerical values widen the students’ learning horizons.
In addition, the subject becomes more inclusively if such objects as pottery that are made in the traditional way are used. They get to have their own way of learning and this does more than favor students who have learning difficulty in abstract thinking where mathematics evidently requires. This approach also enhances creativity and critical thinking since the students are required to think about the geometric outcomes of their designs.
Conclusion
Introducing elementary school children to geometry lessons using traditional pottery is the perfect example of striving for continuity between theoretical knowledge and real-life practices. : It also makes them learn in a way that is educational as well as makes them embrace the different cultural practices. With the incorporation of art, as well as history in the learning process, a teacher can enrich the mathematics learning of students and make it more engaging and meaningful to students’ lives.